Https介绍
HTTPS:为了保证隐私数据能加密传输,采用SSL/TLS协议用于对HTTP协议传输的数据进行加密,也就是HTTPS。
SSL:SSL(Secure Sockets Layer)协议是由网景公司设计,后被IETF定义在RFC 6101中,目前的版本是3.0。
TLS:TLS可以说是SSL的改进版。是由IETF对SSL3.0进行了升级而出现的,定义在RFC 2246,实际上我们现在的HTTPS都是用的TLS协议。
HTTPS在传输数据之前需要客户端(浏览器)与服务端(网站)之间进行一次握手,在握手过程中将确立双方加密传输数据的密码信息;TLS/SSL中使用了非对称加密,对称加密以及HASH算法,其中非对称加密算法用于在握手过程中加密生成的密码,对称加密算法用于对真正传输的数据进行加密,而HASH算法用于验证数据的完整性;TLS握手过程中如果有任何错误,都会使加密连接断开,从而阻止了隐私信息的传输。
SSL/TLS版本
1994年,NetScape公司设计了SSL协议(Secure Sockets Layer)的1.0版,但是未发布;
1995年,NetScape公司发布SSL 2.0版,很快发现有严重漏洞;
1996年,SSL 3.0版问世,得到大规模应用;
1999年,互联网标准化组织ISOC接替NetScape公司,发布了SSL的升级版TLS 1.0版;
2006年和2008年,TLS进行了两次升级,分别为TLS 1.1版和TLS 1.2版。最新的变动是2011年TLS 1.2的修订版。
JDK对SSL/TLS版本的支持
JDK 8(March 2014 to present):TLSv1.2 (default),TLSv1.1,TLSv1,SSLv3
JDK 7(July 2011 to present):TLSv1.2,TLSv1.1,TLSv1 (default),SSLv3
JDK 6(2006 to end of public updates 2013):TLS v1.1 (JDK 6 update 111 and above),TLSv1 (default),SSLv3
更多详细介绍:https://blogs.oracle.com/java-platform-group/diagnosing-tls%2c-ssl%2c-and-https
准备
JDK:jdk1.7.0_80
Tomcat:apache-tomcat-7.0.28
配置Tomcat支持Https
1.生成服务器证书
C:\Users\Administrator.SKY-20170404CXG>cd C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_80\bin
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_80\bin>keytool -genkey -v -alias tomcat -keyalg R
SA -keystore E:\tomcat.keystore
输入密钥库口令:
再次输入新口令:
您的名字与姓氏是什么?
[Unknown]: localhost
您的组织单位名称是什么?
[Unknown]: codingo
您的组织名称是什么?
[Unknown]: codingo
您所在的城市或区域名称是什么?
[Unknown]: nanjing
您所在的省/市/自治区名称是什么?
[Unknown]: jiangsu
该单位的双字母国家/地区代码是什么?
[Unknown]: zhongguo
CN=localhost, OU=codingo, O=codingo, L=nanjing, ST=jiangsu, C=zhongguo是否正确?
[否]: y
正在为以下对象生成 2,048 位RSA密钥对和自签名证书 (SHA256withRSA) (有效期为 90 天
):
CN=localhost, OU=codingo, O=codingo, L=nanjing, ST=jiangsu, C=zhongguo
输入 <tomcat> 的密钥口令
(如果和密钥库口令相同, 按回车):
[正在存储E:\tomcat.keystore]密钥为:111111
名字与姓氏:必须是TOMCAT部署主机的域名或者IP,本地测试直接用localhost,如果不这样设置httpclient4测试的时候会出现如下错误:
Exception in thread "main" javax.net.ssl.SSLException: hostname in certificate didn't match: <localhost> != <codingo>最终生成的服务器证书存储在E:\tomcat.keystore,以上的工作是为Tomcat配置支持https协议做准备。
2.修改配置
Tomcat 安装目录下/conf/server.xml中做如下配置:
<Connector port="8443" protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Protocol"
maxThreads="150" SSLEnabled="true" scheme="https" secure="true"
keystoreFile="E:\\tomcat2.keystore" keystorePass="111111"
clientAuth="false" sslProtocol="TLS" sslEnabledProtocols="TLSv1"/>keystoreFile:服务器证书
keystorePass:证书密码
sslProtocol:要使用的ssl协议,一个值代表多个协议版本,默认值TLS,可选值如下:
SSL :TLSv1
SSLv2 :不可用
SSLv3 :TLSv1
TLS :TLSv1
TLSv1 :TLSv1
TLSv1.1 :TLSv1,TLSv1.1
TLSv1.2 :TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2注:以上可选值也要根据具体使用的jdk版本,参考:JDK对SSL/TLS版本的支持,对应jdk版本不支持启动会出现如下错误:
严重: Failed to initialize end point associated with ProtocolHandler ["http-nio-8443"]
java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException: TLSv1.1 SSLContext not available以上值可以通过如下代码获取:
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, IOException, KeyManagementException {
SSLContext sslcontext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLSv1.1");
sslcontext.init(null, new TrustManager[] { new HttpClient3TrustManager() }, new java.security.SecureRandom());
SSLSocket sslsocket = (SSLSocket) sslcontext.getSocketFactory().createSocket();
String supportedProtocols[] = sslsocket.getSupportedProtocols();
String enabledProtocols[] = sslsocket.getEnabledProtocols();
String sp = "";
String ep = "";
for (String p : supportedProtocols) {
sp = sp + p + ",";
}
for (String p : enabledProtocols) {
ep = ep + p + ",";
}
System.err.println("SupportedProtocols = " + sp + " enabledProtocols = " + ep);
}HttpClient3TrustManager类
public class HttpClient3TrustManager implements X509TrustManager {
public void checkClientTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) throws CertificateException {
}
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) throws CertificateException {
}
public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() {
return new X509Certificate[] {};
}
}sslEnabledProtocols:支持HTTPS连接的SSL协议,用逗号分隔;如果设置值支持的协议就为当前值,否则默认值:TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2
更多参考:
https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-7.0-doc/config/http.html
http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/security/StandardNames.html#SSLContext
浏览器测试
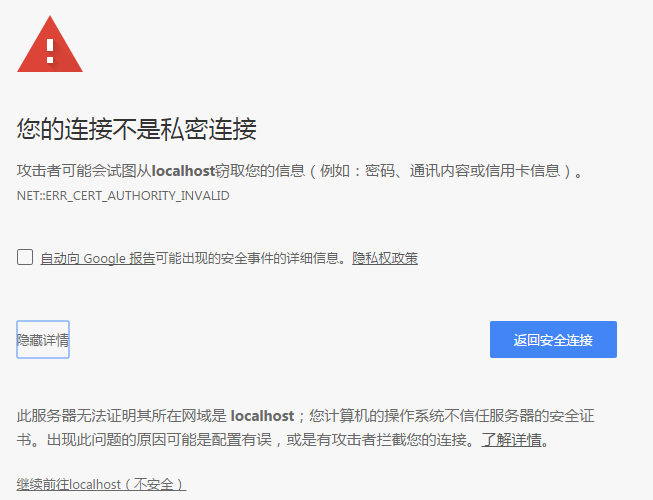
打开chrome浏览器输入地址:https://localhost:8443/,如下图所示:
Httpclient3测试
maven引入httpclient3:
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-httpclient</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-httpclient</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
</dependency>HttpClient3测试类:
public class HttpClient3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("javax.net.debug", "all");
String y = doGet("https://localhost:8443/");
System.out.println(y);
}
public static String doGet(String url) {
StringBuffer response = new StringBuffer();
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
HttpMethod method = new GetMethod(url);
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
if (url.startsWith("https")) {
Protocol myhttps = new Protocol("https", new HttpClient3SSLProtocolSocketFactory(), 443);
Protocol.registerProtocol("https", myhttps);
}
client.executeMethod(method);
if (method.getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK) {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(method.getResponseBodyAsStream(), "utf-8"));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(line);
}
}
} catch (URIException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (reader != null) {
reader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}
method.releaseConnection();
}
return response.toString();
}
}System.setProperty(“javax.net.debug”, “all”); 方便了解通过SSL协议建立网络连接时的全过程;
HttpClient3SSLProtocolSocketFactory类:
public class HttpClient3SSLProtocolSocketFactory implements ProtocolSocketFactory {
private SSLContext sslcontext = null;
private SSLContext createSSLContext() {
SSLContext sslcontext = null;
try {
sslcontext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLSv1");
sslcontext.init(null, new TrustManager[] { new HttpClient3TrustManager() }, new java.security.SecureRandom());
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (KeyManagementException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sslcontext;
}
private SSLContext getSSLContext() {
if (this.sslcontext == null) {
this.sslcontext = createSSLContext();
}
return this.sslcontext;
}
public Socket createSocket(Socket socket, String host, int port, boolean autoClose)
throws IOException, UnknownHostException {
return getSSLContext().getSocketFactory().createSocket(socket, host, port, autoClose);
}
public Socket createSocket(String host, int port) throws IOException, UnknownHostException {
return getSSLContext().getSocketFactory().createSocket(host, port);
}
public Socket createSocket(String host, int port, InetAddress clientHost, int clientPort)
throws IOException, UnknownHostException {
return getSSLContext().getSocketFactory().createSocket(host, port, clientHost, clientPort);
}
public Socket createSocket(String host, int port, InetAddress localAddress, int localPort,
HttpConnectionParams params) throws IOException, UnknownHostException, ConnectTimeoutException {
if (params == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parameters may not be null");
}
SocketFactory socketfactory = getSSLContext().getSocketFactory();
return socketfactory.createSocket(host, port, localAddress, localPort);
}
}来看一下SSL双向认证的全过程(图片来自网上):
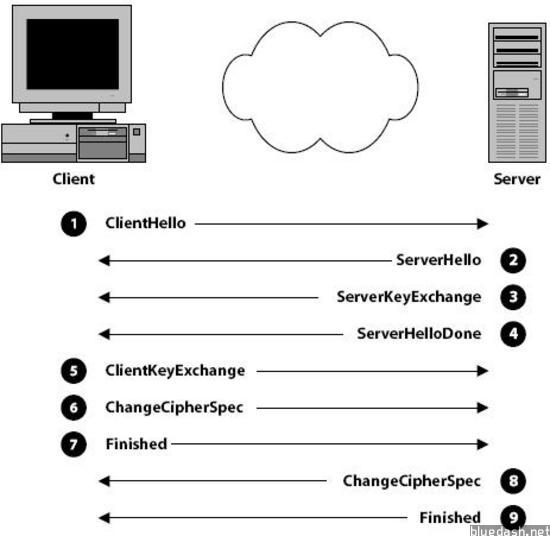
更多详细的介绍wiki:传输层安全协议
下面以上图SSL认证过程,来看具体日志输出,具体模拟几个环境
环境一:
server:jdk1.7,tomcat:apache-tomcat-7.0.28,server.xml配置:sslProtocol=”TLSv1.1″
client:jdk1.7,SSLContext.getInstance(“TLSv1.2”)
运行测试程序,部分日志如下:
*** ClientHello, TLSv1.2
RandomCookie: GMT: 1496977933 bytes = { ... }
Session ID: {}
Cipher Suites: []
Compression Methods: { 0 }
....更多细节运行查看
***客户端告诉服务器:支持的协议版本:TLSv1.2,一个客户端生成的随机数,支持的加密方法,支持的压缩方法;
*** ServerHello, TLSv1.2
RandomCookie: GMT: 1496981693 bytes = { ... }
Session ID: {...}
Cipher Suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
Compression Method: 0
....更多细节运行查看
***服务器回应客户端:确认使用的加密通信协议版本TLSv1.2,一个服务器生成的随机数,确认使用的加密方法,服务器证书;
其他步骤参考上图或者wiki,此处不在列出。
客户端使用TLSv1.2,服务器sslProtocol=”TLSv1.1″,最终确认的通讯版本是TLSv1.2,sslProtocol参数并没有限制TLS的版本,真正起作用的是sslEnabledProtocols参数;
环境二:
server:jdk1.7,tomcat:apache-tomcat-7.0.28,server.xml配置:sslProtocol=”TLS”,sslEnabledProtocols=”TLSv1.1″
client:jdk1.7,SSLContext.getInstance(“TLSv1.2”)
运行测试程序,部分日志如下:
*** ClientHello, TLSv1.2
*** ServerHello, TLSv1.1客户端使用TLSv1.2,服务器端设置了sslEnabledProtocols=”TLSv1.1″,最终以TLSv1.1为准
环境三:
server:jdk1.7,tomcat:apache-tomcat-7.0.28,server.xml配置:sslProtocol=”TLS”,sslEnabledProtocols=”TLSv1.1″
client:jdk1.7,SSLContext.getInstance(“TLSv1”)
客户端报如下错误:
javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: Remote host closed connection during handshake如果配置protocol=”org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Protocol”,异常如下:
javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: Received fatal alert: handshake_failure其他web服务器也可能出现如下异常:
javax.net.ssl.SSLException: Received fatal alert: protocol_version原因分析:客户端设置的版本低于sslEnabledProtocols中指定的版本
Httpclient4测试
maven引入httpclient4:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
<version>4.3.6</version>
</dependency>HttpClient4测试类:
public class HttpClient4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.setProperty("javax.net.debug", "all");
SSLContext sslContext = new SSLContextBuilder().loadTrustMaterial(null, new TrustStrategy() {
public boolean isTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) throws CertificateException {
return true;
}
}).build();
SSLConnectionSocketFactory sslsf = new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(sslContext,
new String[] { "TLSv1" }, null,
SSLConnectionSocketFactory.BROWSER_COMPATIBLE_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER);
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom().setSSLSocketFactory(sslsf).build();
HttpGet get = new HttpGet();
get.setURI(new URI("https://localhost:8443/"));
httpClient.execute(get);
}
}总结
介绍了ssl/tls相关概念,配置tomcat7用来支持https,然后以httpclient3和4为客户端忽略证书验证访问服务器端,通过日志查看ssl/tls握手流程;并且模拟了多种环境用来测试ssl/tls版本,以及可能出现的一些问题。