Dubbo是什么
Dubbo是一个分布式服务框架,致力于提供高性能和透明化的RPC远程服务调用方案,以及SOA服务治理方案;
其核心部分包含:
远程通讯:提供对多种基于长连接的NIO框架抽象封装,包括多种线程模型,序列化,以及“请求-响应”模式的信息交换方式。
集群容错:提供基于接口方法的透明远程过程调用,包括多协议支持,以及软负载均衡,失败容错,地址路由,动态配置等集群支持。
自动发现:基于注册中心目录服务,使服务消费方能动态的查找服务提供方,使地址透明,使服务提供方可以平滑增加或减少机器。
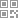
架构图如下:来自官网
Provider: 暴露服务的服务提供方。
Consumer: 调用远程服务的服务消费方。
Registry: 服务注册与发现的注册中心。
Monitor: 统计服务的调用次调和调用时间的监控中心。
Container: 服务运行容器。
与Spring和Zookeeper的集成测试
从上面的架构图中了解到整个系统需要5个部分,不过此处为了方便测试,只提供了Provider,Consumer以及Registry三个部分;代码结构图如下所示:
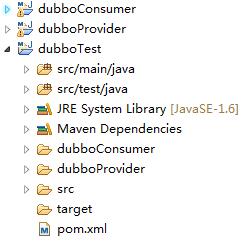
dubboTest是公共的父工程,dubboProvider和dubboConsumer分别是其子工程,分别对应了Provider和Consumer两个部分,至于Registry由Zookeeper来支持,下面详细介绍每一部分。
1.公共maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>4.3.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId>
<artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId>
<version>3.4.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.sgroschupf</groupId>
<artifactId>zkclient</artifactId>
<version>0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
<version>2.5.3</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>主要是Spring,Zookeeper以及dubbo相关的包
2.Provider相关介绍
提供一个对外的接口类DemoService
public interface DemoService {
String syncSayHello(String name);
String asyncSayHello(String name);
}提供DemoService的实现类DemoServiceImpl
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
@Override
public String syncSayHello(String name) {
return "sync Hello " + name;
}
@Override
public String asyncSayHello(String name) {
return "async Hello " + name;
}
}提供provider配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:dubbo="http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo
http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- 提供方应用信息,用于计算依赖关系 -->
<dubbo:application name="hello-world-app" />
<!-- 使用zookeeper注册中心暴露服务地址 -->
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181" />
<!-- 用dubbo协议在20880端口暴露服务 -->
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880" />
<!-- 声明需要暴露的服务接口 -->
<dubbo:service interface="org.dubboProvider.DemoService"
ref="demoService" />
<!-- 和本地bean一样实现服务 -->
<bean id="demoService" class="org.dubboProvider.DemoServiceImpl" />
</beans> dubbo:registry:提供了注册中心,为了方便此处配置的是本地的zookeeper
dubbo:service:提供了对外的服务接口
提供Provider启动类Provider
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Provider {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
new String[] { "dubbo-provider.xml" });
context.start();
System.in.read(); // 按任意键退出
}
}3.Consumer相关介绍
Consumer配置文件dubbo-consumer.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:dubbo="http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo
http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- 消费方应用名,用于计算依赖关系,不是匹配条件,不要与提供方一样 -->
<dubbo:application name="consumer-of-helloworld-app" />
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181" />
<!-- 生成远程服务代理,可以和本地bean一样使用demoService -->
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" interface="org.dubboProvider.DemoService" >
<dubbo:method name="syncSayHello" async="false" />
<dubbo:method name="asyncSayHello" async="true" />
</dubbo:reference>
</beans> Consumer测试类Consumer
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import org.dubboProvider.DemoService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcContext;
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException,
ExecutionException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"dubbo-consumer.xml");
context.start();
DemoService demoService = (DemoService) context.getBean("demoService"); // 获取远程服务代理
System.out.println(demoService.syncSayHello("world"));
System.out.println(demoService.asyncSayHello("world"));
Future<String> futrue = RpcContext.getContext().getFuture();
System.out.println(futrue.get());
}
}运行Consumer类,结果如下:
sync Hello world
null
async Hello world
调用流程简要分析
1.启动Provider,读取配置文件
Provider启动向Zookeeper中注册服务器的相关信息,主要的接口类RegistryService,四个实现类分别是:ZookeeperRegistry,RedisRegistry,DubboRegistry以及MulticastRegistry,这里使用的是ZookeeperRegistry,启动Provider的时候会调用doRegistry()方法,代码如下:
protected void doRegister(URL url) {
try {
zkClient.create(toUrlPath(url), url.getParameter(Constants.DYNAMIC_KEY, true));
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to register " + url + " to zookeeper " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}url详细信息:dubbo://192.168.67.13:20880/org.dubboProvider.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=hello-world-app&dubbo=2.5.3&interface=org.dubboProvider.DemoService&methods=syncSayHello,asyncSayHello&pid=4952&side=provider×tamp=1487671777581
通过zkclient在Zookeeper上创建节点,为Consumer获取节点做准备。
2.启动Consumer,读取配置文件
监听Zookeeper中注册的服务器信息节点,通过节点信息建立和远程服务器的连接,所有的客户端都继承于AbstractClient,对应的实现类有NettyClient,MinaClient以及GrizzlyClient;3个都是基于java nio的底层通信框架,默认使用的是NettyClient,在AbstractClient的构造方法中就建立了和服务器的连接,部分代码如下:
public AbstractClient(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
//...省略...
connect();
//...省略...
}对应的在NettyClient中进行了doConnect()
protected void doConnect() throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(getConnectAddress());
//...省略...
NettyClient.this.channel = newChannel;
//...省略...
}NettyClient中保存了建立的连接。
3.生成动态代理
通过简单的接口调用就实现了远程方法的调用,其实就是dubbo帮助我们生成了一个动态代理类,所有的关于建立远程连接,消息封装编码,消息的发送以及消息的接收解码都在动态代理类里面帮我们处理了
dubbo提供的代理工厂类都继承于AbstractProxyFactory类,对应的实现类有JdkProxyFactory和JavassistProxyFactory,默认情况下使用的JavassistProxyFactory,相应代码如下:
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}4.方法调用触发InvokerInvocationHandler调用invoke方法
invoke方法代码如下:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(invoker, args);
}
if ("toString".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.toString();
}
if ("hashCode".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.hashCode();
}
if ("equals".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 1) {
return invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
return invoker.invoke(new RpcInvocation(method, args)).recreate();
}RpcInvocation用来封装了方法调用的相关参数比如:方法名,参数类型,参数列表等,可以查看相关代码:
public class RpcInvocation implements Invocation, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4355285085441097045L;
private String methodName;
private Class<?>[] parameterTypes;
private Object[] arguments;
private Map<String, String> attachments;
private transient Invoker<?> invoker;
......//以下省略经过层层调用最后到达了DubboInvoker的doInvoke方法中,也是我们比较关心的类,代码如下:
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) invocation;
final String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
inv.setAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY, getUrl().getPath());
inv.setAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY, version);
ExchangeClient currentClient;
if (clients.length == 1) {
currentClient = clients[0];
} else {
currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length];
}
try {
boolean isAsync = RpcUtils.isAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation);
int timeout = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY,Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
if (isOneway) {
boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false);
currentClient.send(inv, isSent);
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);
return new RpcResult();
} else if (isAsync) {
ResponseFuture future = currentClient.request(inv, timeout) ;
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(new FutureAdapter<Object>(future));
return new RpcResult();
} else {
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);
return (Result) currentClient.request(inv, timeout).get();
}
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION, "Invoke remote method timeout. method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.NETWORK_EXCEPTION, "Failed to invoke remote method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}里面有我们比较关心的同步和异步调用:
同步调用:调用ResponseFuture的get()方法进行等待服务器的返回
异步调用:没有等待服务器的返回,直接将ResponseFuture放入了RpcContext.getContext()中,这也是我们需要在代码中使用Future futrue = RpcContext.getContext().getFuture();的原因。
5.发送请求
在第二步中已经建立了和远程服务器的连接,建立的数量和集群的服务器有关,所以客户端是一个数组,从数组中获取一个客户端连接
if (clients.length == 1) {
currentClient = clients[0];
} else {
currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length];
}获取之后执行currentClient.request(inv, timeout),就是对服务器发送请求,进入到request方法中有如下代码:
public ResponseFuture request(Object request, int timeout) throws RemotingException {
if (closed) {
throw new RemotingException(this.getLocalAddress(), null, "Failed to send request " + request + ", cause: The channel " + this + " is closed!");
}
// create request.
Request req = new Request();
req.setVersion("2.0.0");
req.setTwoWay(true);
req.setData(request);
DefaultFuture future = new DefaultFuture(channel, req, timeout);
try{
channel.send(req);
}catch (RemotingException e) {
future.cancel();
throw e;
}
return future;
}把要发送的消息封装成了一个Request对象,并且返回了DefaultFuture(继承于ResponseFuture实现了同步和异步的调用),可以看一下DefaultFuture的get()方法:
public Object get(int timeout) throws RemotingException {
if (timeout <= 0) {
timeout = Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT;
}
if (! isDone()) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
lock.lock();
try {
while (! isDone()) {
done.await(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (isDone() || System.currentTimeMillis() - start > timeout) {
break;
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
if (! isDone()) {
throw new TimeoutException(sent > 0, channel, getTimeoutMessage(false));
}
}
return returnFromResponse();
}while一直在循环,直到isDone为true,或者超时了,isDone其实就是判断response是否为空:
public boolean isDone() {
return response != null;
}6.接收消息
DefaultFuture中的received()用来接收消息同时赋值给了Response response,这样isDone()方法可以为true了
总结
以上只是对dubbo粗浅的使用,以及简单的了解了一下调用的整个流程,没有太多更加的深入,主要还是项目没有实际用到;不过可以看到dubbo底层通信是基于netty,mina这种高性能的通信框架,而且通过长连接减少握手;二进制流压缩数据,比常规HTTP等短连接协议更快,这个上面没有提到,更多的可以查看编解码类DubboCodec;可以认为dubbo的性能还是相当强的。